If you’re dealing with frequent back or neck pain, your posture might be playing a bigger role than you think. Whether you're sitting at a desk all day or scrolling on your phone for hours,…
Coccydynia, sometimes referred to as tailbone pain, can be an uncomfortable, even debilitating condition. Undoubtedly, severe tailbone pain can make sitting or even standing for long periods of time very difficult.
You’re probably wondering what causes this peculiar type of pain. And, more importantly, how you can treat it. Luckily, there are some easy things that you can do to relieve an inflamed coccyx. Use this guide to understand coccydynia and discover ways to conquer the pain.
Understanding the Tailbone
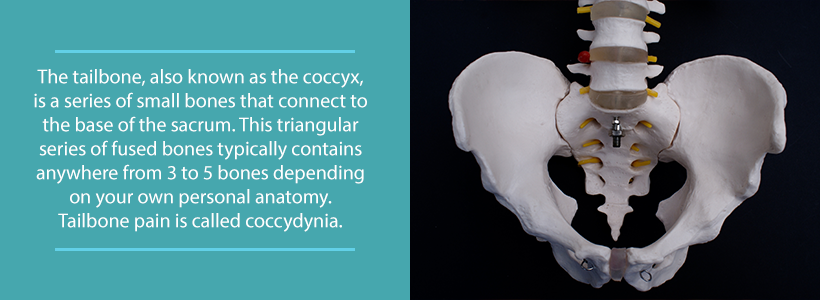
The tailbone, formally referred to as the coccyx, is a series of small bones connected to the sacrum through the sacrococcygeal joint. Located at the base of the lower back, the sacrum forms the back of the pelvic wall and keeps the pelvis stable. The coccyx is the triangular-shaped mass of bone that resides directly below the sacrum. It is usually only a few inches long.
A person may have three to five coccyx bones depending on their development. These bones are fused together by small joints or disc-like ligaments. This fusion allows for some movement when sitting or standing.
Likewise, the coccyx aids in support and weight distribution when a person is seated. In addition, many pelvic floor muscles are connected to the tailbone. These muscles help with leg movements such as walking and running. They also support various functions of the anus and vagina.
If the coccyx joints or bones become damaged or inflamed, it could lead to a painful condition known as coccydynia. So how could such a small bone mass cause such major pain? Let’s look at a few common causes.
Causes of Coccydynia
Coccyx pain can occur for a variety of reasons. It is usually caused by too much or too little movement in the area. These mobility issues can apply stress to the joints, leading to pain, nearby muscle tension, pelvic floor spasms, and inflammation.
In many cases, tailbone pain occurs because of trauma or injury to the area. A bad fall can result in inflammation around the coccyx, causing further discomfort. Activities that apply prolonged pressure to the tailbone can also be to blame. This includes sitting on hard surfaces for a long time or even horseback riding. Obesity also puts a person at a higher risk for developing coccydynia symptoms.
In addition, as we age, normal wear and tear on the body can cause painful inflammation in the joints. Furthermore, degenerative joint disease can occur anywhere in the body—including the coccyx. Prior injuries to the area can also hasten the disease progression.
Moreover, gender also plays a role. In fact, women are up to 5 times more likely to suffer tailbone pain. Why women? Their anatomy generally allows for less pelvic rotation which can lead to coccyx injury. Childbirth can also be to blame. As the baby moves over the tailbone during vaginal birth, the coccyx may suffer injuries.
In rare cases, cancer or an infection of the area may cause tailbone pain. Cancer usually starts in a different area of the body, such as the prostate, cervix, or ovaries. For some, it spreads to the coccyx. An infection of the coccyx could also cause unique symptoms that require a doctor’s care.
Symptoms of Coccydynia
You’re probably wondering how you can differentiate coccyx pain from other lower back conditions. It may be easier than you think. For example, tailbone pain usually persists in a specific area. It doesn’t radiate outward to other areas of the body like the legs or feet.
Symptoms of coccydynia include:
- Pain and tenderness are confined to the tailbone area. This can be an aching throb that ranges in intensity from mild to severe.
- Tightness around the tailbone. Sometimes this sensation can be constant. Other times it comes and goes depending on your activities.
- Increased pain while seated. Putting weight on the tailbone, especially while sitting on hard surfaces, can cause even more pain.
- Difficulty changing positions. Those with coccydynia often feel pain while sitting down or getting up from a seated position.
- Pain during bowel movements or sexual intercourse. Since the coccyx is so close to the anus and genitals, these activities may cause spikes in pain.
- Swelling, redness, or drainage near your tailbone. These symptoms can indicate an infection in the area, which often requires a doctor’s care.
Pain Management and Coccydynia Treatments
Luckily, for most people, non-surgical treatments are effective at reducing tailbone pain. Here are some things you can do to help manage your coccydynia:
Lifestyle Modifications
Making simple changes to your daily habits can make a big difference. For example, try to avoid sitting for long periods of time. If you have a desk job, get up and walk around for a few minutes every hour. In addition, adjust your posture when seated. Leaning forward while sitting can help take pressure off the coccyx. You can also buy a specially designed coccyx cushion (found online or at many drug stores).
Since obesity may be a factor in your coccyx pain, consider taking time each day to exercise. This can help with weight loss and strengthen the muscles surrounding the coccyx area. In addition, aerobic activity helps to release the body’s natural endorphins—pain-relieving chemicals.
If you feel pain while having bowel movements, try to eat a diet rich in high-fiber foods. Also, don’t forget to stay hydrated. These dietary changes can help to soften the stool so that it’s easier and less painful to have a bowel movement. If necessary, take a stool softener or laxative if you continue to have painful bowel movements.
Use Cold Packs or Heating Pads
Just like many other muscular or orthopedic injuries, heat and cold can provide relief. Using a cold pack several times a day during a painful flare-up can reduce inflammation. A heat source like a hot water bottle, warm bath, or heating pad may also provide soothing relief. Heat typically reduces muscle tension to the affected area and increases blood flow.
Experiment with hot and cold treatments to see which combinations work best for you.
Medications
If lifestyle changes and cold packs or heating pads aren’t giving you the necessary relief, then medications may be your next step. Luckily, over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen can be very effective. These medications can reduce inflammation and ease the pain.
For more severe cases, a doctor may order prescription pain medications. These medications can be effective for some, but they also may be habit-forming or lead to adverse side effects for others. Another option is a steroidal injection. Your doctor will administer the shot, which is a combination of a numbing agent and a steroid, to decrease inflammation.
Manual Manipulation of the Coccyx Area
Chiropractic care can allow for adjustment of the sacrococcygeal joint. This can reduce the pain caused by poor joint mobility. In addition, some people find relief with massage. Specially trained massage therapists can work on tense pelvic floor muscles with deep tissue massage.
Physical Therapy may also prove beneficial. A physical therapist can suggest an exercise routine that gently stretches the ligaments in the coccyx area. In addition, a PT can suggest modifications to your daily activities which will prevent painful flare-ups.
A doctor or physical therapist may also use a Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulator (TENS) unit. This is a small device that uses electrical stimulation to disrupt tailbone pain signals from reaching the brain. It is a good option for those who would rather not use pain medications.
Surgical Treatments
Most people don’t need surgery for coccydynia. There are some individuals, however, that don’t respond to conservative treatments. If you tried several of the above pain management techniques for at least two months without results, then your doctor may consider surgery.
A coccygectomy is the typical surgical option. This involves removing part or all of the coccyx. The procedure is quick and straightforward. In many cases, it is minimally invasive. This means a small incision is used to gain access to the area and remove the coccyx. Minimally invasive surgery offers several benefits, including quicker recovery times, less damage to the body, and minimal scarring.
Such procedures generally achieve good outcomes after the initial healing process. Due to the complicated nature of the surgery, the recovery period may last anywhere from three months to a year.
Ready to Get Help for Your Coccydynia?
If you tried conservative treatments and still suffer from tailbone pain, then you may need the guidance of an orthopedic doctor. These doctors specialize in pinpointing the source of pain and finding the best treatment options based on your specific needs and goals.
Orthopedic & Laser Spine Surgery uses the most advanced and minimally invasive techniques to help you manage your pain. Our doctors believe appropriate conservative treatments should be considered before exploring surgical options. If you do need surgery, then our team has the experience and technology to ensure that you are receiving quality care for your tailbone pain.
Are you ready to once again start enjoying your life without the burden of pain? A simple call to (855) 853-6542 puts you in contact with a team of dedicated professionals who are ready to help you get back to the life you want. Calling now may be the first step toward enjoying a pain-free future.